Plant and animal cell parts and functions pdf
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
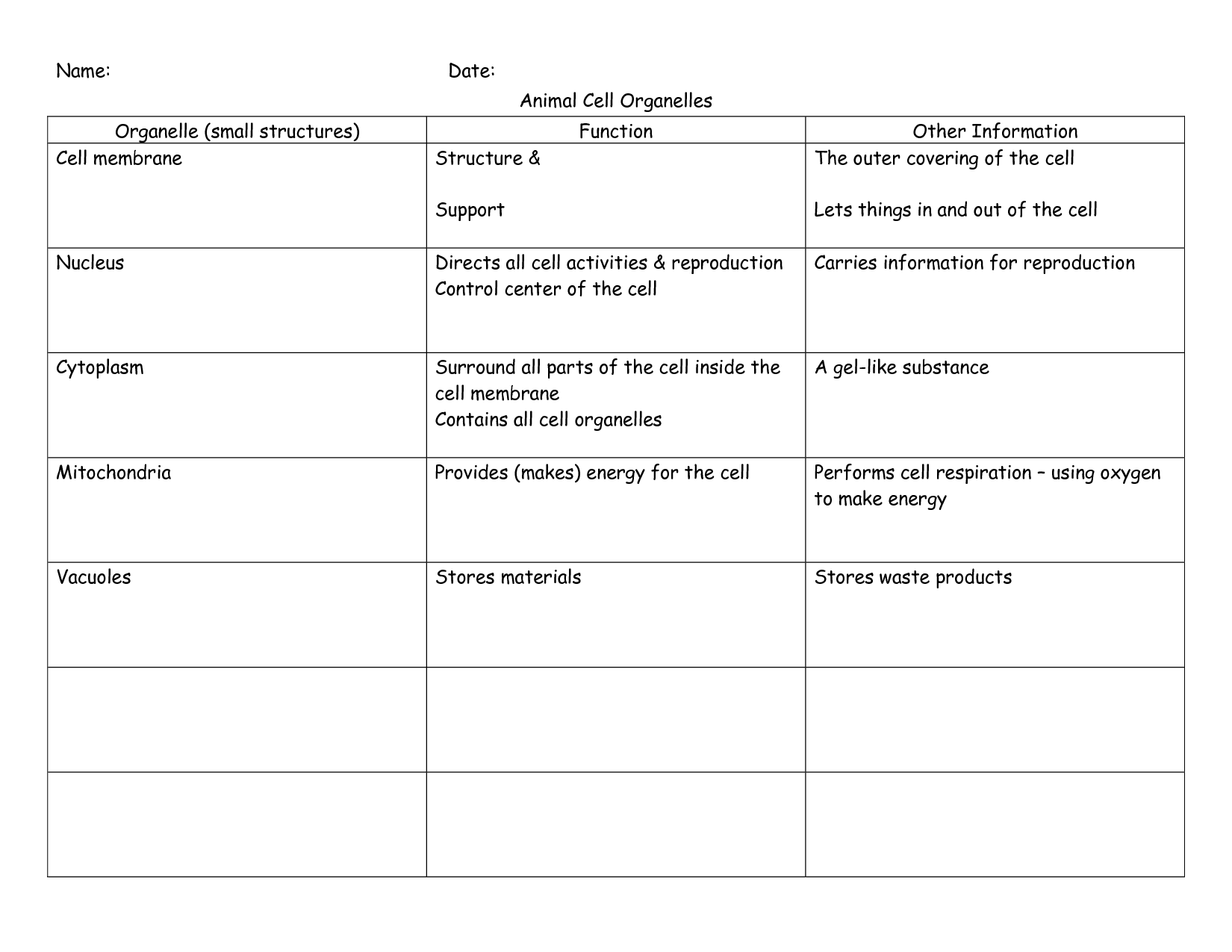
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
The plasmodesmata, pores in the cell wall that link adjacent cells and allow plant cells to communicate with adjacent cells. Animals have a different but functionally analogous system of gap junctions between adjacent cells.
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
11/07/2012 · Plant cells have to perform two functions that are not required of animal cells: Produce their own food (which they do in a process called photosynthesis ). Support their own weight (which animals usually do by means of a skeleton).
and function of the organelles in plant and animal cells. Summary: This lesson is designed to teach the students about cell organelles and their functions within plant and animal cells.
We will explore several interactive websites that will show us all the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. We will learn how to identify all the parts and differentiate between an animal cell and a plant cell. We will also learn the functions of all the parts of the cell. There are additional
Animal and Plant Cell Venn Diagram 6 Cell Organelles 7 The Animal Cell 8 If you think about it, your local community has many parts that allow it to function properly, just like an plant cell. Relate the functions of a plants cell’s organelles to parts of your community that have a similar function. Organelle Function of organelle in the cell Name a part of your school that has a similar
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
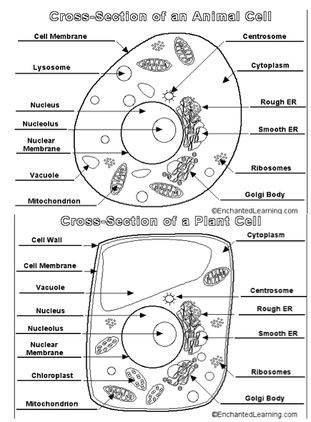
The student will distinguish between plant and animal cells. Day 1: Introduction to Plant Cells Objectives: Students will be able to correctly identify key parts on a cell. Students will be able to correctly identify plant cells. Students will be able to correctly identify animal cells. Materials: • Computer • Overhead • Plant cell pictures • Animal cell pictures • Diagram of cells
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
the same function in both plant and animal cells. The cell membrane has transport proteins to assist the passage oflarger molecules or ionized molecUles. There are avariety ofother proteins embedded in the cell membrane. These are known as integralproteins. They help to maintain the structure ofthe cell membrane and other important functions. Sometimes the integral proteins have auxiliary
I can label parts of animal and plant cells the tasks and functions of life. The Cell Theory All living organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The Cell Theory. ①Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus Examples: bacteria ②Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and
Grade 7 Science Unit 2 Plant and Animal Cells
https://youtube.com/watch?v=nGeTaeZaYdw

Biology Plant & Animal Cells III (Parts & Functions
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
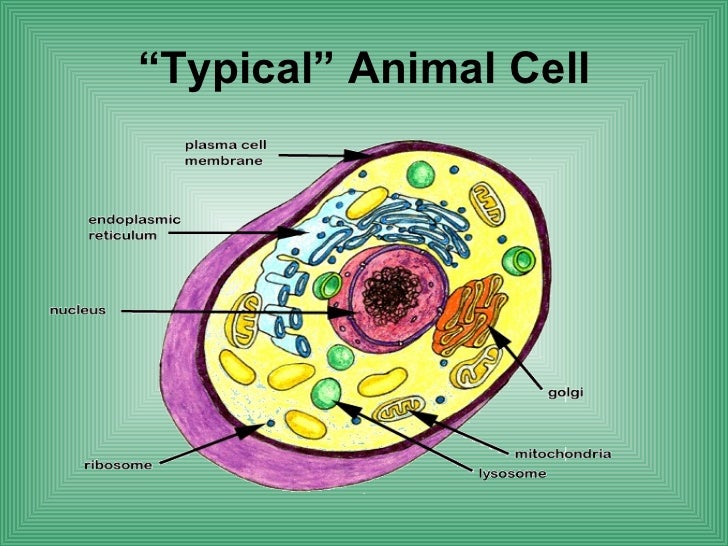
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
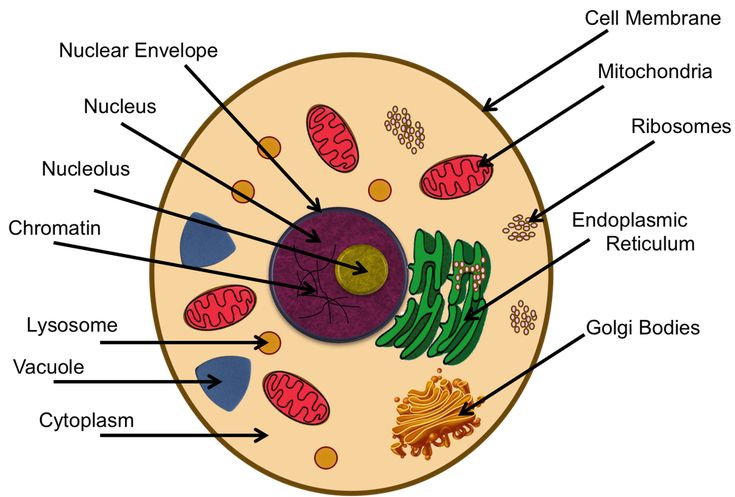
This is a basic illustration of a plant cell with major parts labeled. Labels include nucleus, chloroplast, cytoplasm, membrane, cell wall, and vacuole, and mitochondrion. Use it as a poster in your classroom or have students glue it into their science notebooks.
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; these are organelles pertinent to plant cells. In the title “Animal Cell Parts and Functions”, the word “Part” pertains to “Organelles”; these are specialized parts inside a living cell.
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
goes out, gives shape and support, plant cell, animal cell); understand and use the English expressions for describing the functions of the different parts of a cell, e.g., Different parts of a cell carry out different activities so that the cell can function normally. The nucleus is the place which controls the activities of a cell. It also contains DNA, which carries the information for
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Title: PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL 1 PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL. How do plant cells differ from animal cells? By Miss Caparos ; 2 Do Now. Identify the structures and state its function.
Organelles found in both animal and plant cells: The cell membrane (or plasma membrane) is the ‘skin’ that surrounds the entire cell. This porous membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids (phospholipid bilayer). The membrane allows the passage of nonpolar and small uncharged polar molecules via diffusion, while other larger polar molecules and ions are able to enter the cell
https://youtube.com/watch?v=8IlzKri08kk
CELLS kean.edu
Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells ThoughtCo
Cell Parts and Functions CPALMS.org
PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL PowerShow.com
https://youtube.com/watch?v=5byUPiZr-7s
Directions for Animal Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy

4.5 Plant and Animal Cells WordPress.com
WebQuest Plant and Animal Cells Zunal.Com

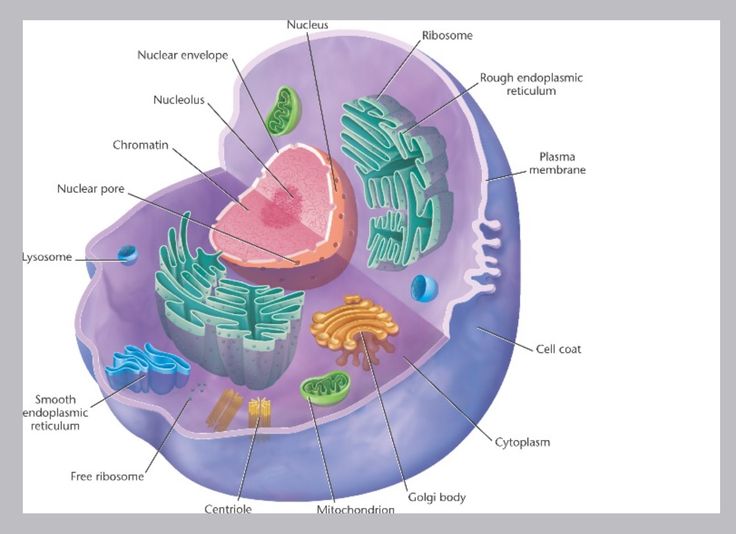
https://youtube.com/watch?v=5rAWPOR-F2E
Cell Parts and Functions CPALMS.org
Directions for Animal Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
We will explore several interactive websites that will show us all the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. We will learn how to identify all the parts and differentiate between an animal cell and a plant cell. We will also learn the functions of all the parts of the cell. There are additional
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
Title: PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL 1 PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL. How do plant cells differ from animal cells? By Miss Caparos ; 2 Do Now. Identify the structures and state its function.
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
Directions for Animal Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy
Cell Parts and Functions CPALMS.org
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
The student will distinguish between plant and animal cells. Day 1: Introduction to Plant Cells Objectives: Students will be able to correctly identify key parts on a cell. Students will be able to correctly identify plant cells. Students will be able to correctly identify animal cells. Materials: • Computer • Overhead • Plant cell pictures • Animal cell pictures • Diagram of cells
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; these are organelles pertinent to plant cells. In the title “Animal Cell Parts and Functions”, the word “Part” pertains to “Organelles”; these are specialized parts inside a living cell.
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
This is a basic illustration of a plant cell with major parts labeled. Labels include nucleus, chloroplast, cytoplasm, membrane, cell wall, and vacuole, and mitochondrion. Use it as a poster in your classroom or have students glue it into their science notebooks.
Directions for Animal Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy
CELLS kean.edu
goes out, gives shape and support, plant cell, animal cell); understand and use the English expressions for describing the functions of the different parts of a cell, e.g., Different parts of a cell carry out different activities so that the cell can function normally. The nucleus is the place which controls the activities of a cell. It also contains DNA, which carries the information for
Animal and Plant Cell Venn Diagram 6 Cell Organelles 7 The Animal Cell 8 If you think about it, your local community has many parts that allow it to function properly, just like an plant cell. Relate the functions of a plants cell’s organelles to parts of your community that have a similar function. Organelle Function of organelle in the cell Name a part of your school that has a similar
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
11/07/2012 · Plant cells have to perform two functions that are not required of animal cells: Produce their own food (which they do in a process called photosynthesis ). Support their own weight (which animals usually do by means of a skeleton).
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
the same function in both plant and animal cells. The cell membrane has transport proteins to assist the passage oflarger molecules or ionized molecUles. There are avariety ofother proteins embedded in the cell membrane. These are known as integralproteins. They help to maintain the structure ofthe cell membrane and other important functions. Sometimes the integral proteins have auxiliary
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; these are organelles pertinent to plant cells. In the title “Animal Cell Parts and Functions”, the word “Part” pertains to “Organelles”; these are specialized parts inside a living cell.
Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells ThoughtCo
Biology Plant & Animal Cells III (Parts & Functions
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
goes out, gives shape and support, plant cell, animal cell); understand and use the English expressions for describing the functions of the different parts of a cell, e.g., Different parts of a cell carry out different activities so that the cell can function normally. The nucleus is the place which controls the activities of a cell. It also contains DNA, which carries the information for
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; these are organelles pertinent to plant cells. In the title “Animal Cell Parts and Functions”, the word “Part” pertains to “Organelles”; these are specialized parts inside a living cell.
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
The student will distinguish between plant and animal cells. Day 1: Introduction to Plant Cells Objectives: Students will be able to correctly identify key parts on a cell. Students will be able to correctly identify plant cells. Students will be able to correctly identify animal cells. Materials: • Computer • Overhead • Plant cell pictures • Animal cell pictures • Diagram of cells
The plasmodesmata, pores in the cell wall that link adjacent cells and allow plant cells to communicate with adjacent cells. Animals have a different but functionally analogous system of gap junctions between adjacent cells.
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
Organelles found in both animal and plant cells: The cell membrane (or plasma membrane) is the ‘skin’ that surrounds the entire cell. This porous membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids (phospholipid bilayer). The membrane allows the passage of nonpolar and small uncharged polar molecules via diffusion, while other larger polar molecules and ions are able to enter the cell
Cell Parts and Functions CPALMS.org
4.5 Plant and Animal Cells WordPress.com
goes out, gives shape and support, plant cell, animal cell); understand and use the English expressions for describing the functions of the different parts of a cell, e.g., Different parts of a cell carry out different activities so that the cell can function normally. The nucleus is the place which controls the activities of a cell. It also contains DNA, which carries the information for
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
and function of the organelles in plant and animal cells. Summary: This lesson is designed to teach the students about cell organelles and their functions within plant and animal cells.
We will explore several interactive websites that will show us all the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. We will learn how to identify all the parts and differentiate between an animal cell and a plant cell. We will also learn the functions of all the parts of the cell. There are additional
The plasmodesmata, pores in the cell wall that link adjacent cells and allow plant cells to communicate with adjacent cells. Animals have a different but functionally analogous system of gap junctions between adjacent cells.
Title: PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL 1 PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL. How do plant cells differ from animal cells? By Miss Caparos ; 2 Do Now. Identify the structures and state its function.
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
I can label parts of animal and plant cells the tasks and functions of life. The Cell Theory All living organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The Cell Theory. ①Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus Examples: bacteria ②Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
CELLS kean.edu
Cell Parts and Functions CPALMS.org
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
and function of the organelles in plant and animal cells. Summary: This lesson is designed to teach the students about cell organelles and their functions within plant and animal cells.
the same function in both plant and animal cells. The cell membrane has transport proteins to assist the passage oflarger molecules or ionized molecUles. There are avariety ofother proteins embedded in the cell membrane. These are known as integralproteins. They help to maintain the structure ofthe cell membrane and other important functions. Sometimes the integral proteins have auxiliary
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
I can label parts of animal and plant cells the tasks and functions of life. The Cell Theory All living organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The Cell Theory. ①Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus Examples: bacteria ②Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
Cell Parts and Functions CPALMS.org
Grade 7 Science Unit 2 Plant and Animal Cells
goes out, gives shape and support, plant cell, animal cell); understand and use the English expressions for describing the functions of the different parts of a cell, e.g., Different parts of a cell carry out different activities so that the cell can function normally. The nucleus is the place which controls the activities of a cell. It also contains DNA, which carries the information for
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
The plasmodesmata, pores in the cell wall that link adjacent cells and allow plant cells to communicate with adjacent cells. Animals have a different but functionally analogous system of gap junctions between adjacent cells.
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
We will explore several interactive websites that will show us all the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. We will learn how to identify all the parts and differentiate between an animal cell and a plant cell. We will also learn the functions of all the parts of the cell. There are additional
the same function in both plant and animal cells. The cell membrane has transport proteins to assist the passage oflarger molecules or ionized molecUles. There are avariety ofother proteins embedded in the cell membrane. These are known as integralproteins. They help to maintain the structure ofthe cell membrane and other important functions. Sometimes the integral proteins have auxiliary
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
and function of the organelles in plant and animal cells. Summary: This lesson is designed to teach the students about cell organelles and their functions within plant and animal cells.
Biology Plant & Animal Cells III (Parts & Functions
Directions for Animal Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
The student will distinguish between plant and animal cells. Day 1: Introduction to Plant Cells Objectives: Students will be able to correctly identify key parts on a cell. Students will be able to correctly identify plant cells. Students will be able to correctly identify animal cells. Materials: • Computer • Overhead • Plant cell pictures • Animal cell pictures • Diagram of cells
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
I can label parts of animal and plant cells the tasks and functions of life. The Cell Theory All living organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The Cell Theory. ①Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus Examples: bacteria ②Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and
CELLS kean.edu
WebQuest Plant and Animal Cells Zunal.Com
This is a basic illustration of a plant cell with major parts labeled. Labels include nucleus, chloroplast, cytoplasm, membrane, cell wall, and vacuole, and mitochondrion. Use it as a poster in your classroom or have students glue it into their science notebooks.
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
11/07/2012 · Plant cells have to perform two functions that are not required of animal cells: Produce their own food (which they do in a process called photosynthesis ). Support their own weight (which animals usually do by means of a skeleton).
the same function in both plant and animal cells. The cell membrane has transport proteins to assist the passage oflarger molecules or ionized molecUles. There are avariety ofother proteins embedded in the cell membrane. These are known as integralproteins. They help to maintain the structure ofthe cell membrane and other important functions. Sometimes the integral proteins have auxiliary
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell.
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
Organelles found in both animal and plant cells: The cell membrane (or plasma membrane) is the ‘skin’ that surrounds the entire cell. This porous membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids (phospholipid bilayer). The membrane allows the passage of nonpolar and small uncharged polar molecules via diffusion, while other larger polar molecules and ions are able to enter the cell
I can label parts of animal and plant cells the tasks and functions of life. The Cell Theory All living organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The Cell Theory. ①Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus Examples: bacteria ②Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and
goes out, gives shape and support, plant cell, animal cell); understand and use the English expressions for describing the functions of the different parts of a cell, e.g., Different parts of a cell carry out different activities so that the cell can function normally. The nucleus is the place which controls the activities of a cell. It also contains DNA, which carries the information for
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
Grade 7 Science Unit 2 Plant and Animal Cells
CELLS kean.edu
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
11/07/2012 · Plant cells have to perform two functions that are not required of animal cells: Produce their own food (which they do in a process called photosynthesis ). Support their own weight (which animals usually do by means of a skeleton).
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
Title: PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL 1 PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL. How do plant cells differ from animal cells? By Miss Caparos ; 2 Do Now. Identify the structures and state its function.
I can label parts of animal and plant cells the tasks and functions of life. The Cell Theory All living organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The Cell Theory. ①Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus Examples: bacteria ②Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and
Organelles found in both animal and plant cells: The cell membrane (or plasma membrane) is the ‘skin’ that surrounds the entire cell. This porous membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids (phospholipid bilayer). The membrane allows the passage of nonpolar and small uncharged polar molecules via diffusion, while other larger polar molecules and ions are able to enter the cell
PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL PowerShow.com
WebQuest Plant and Animal Cells Zunal.Com
Animal and Plant Cell Venn Diagram 6 Cell Organelles 7 The Animal Cell 8 If you think about it, your local community has many parts that allow it to function properly, just like an plant cell. Relate the functions of a plants cell’s organelles to parts of your community that have a similar function. Organelle Function of organelle in the cell Name a part of your school that has a similar
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; these are organelles pertinent to plant cells. In the title “Animal Cell Parts and Functions”, the word “Part” pertains to “Organelles”; these are specialized parts inside a living cell.
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
Cell Parts and Functions CPALMS.org
Biology Plant & Animal Cells III (Parts & Functions
The student will distinguish between plant and animal cells. Day 1: Introduction to Plant Cells Objectives: Students will be able to correctly identify key parts on a cell. Students will be able to correctly identify plant cells. Students will be able to correctly identify animal cells. Materials: • Computer • Overhead • Plant cell pictures • Animal cell pictures • Diagram of cells
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; these are organelles pertinent to plant cells. In the title “Animal Cell Parts and Functions”, the word “Part” pertains to “Organelles”; these are specialized parts inside a living cell.
Organelles found in both animal and plant cells: The cell membrane (or plasma membrane) is the ‘skin’ that surrounds the entire cell. This porous membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids (phospholipid bilayer). The membrane allows the passage of nonpolar and small uncharged polar molecules via diffusion, while other larger polar molecules and ions are able to enter the cell
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
and function of the organelles in plant and animal cells. Summary: This lesson is designed to teach the students about cell organelles and their functions within plant and animal cells.
11/07/2012 · Plant cells have to perform two functions that are not required of animal cells: Produce their own food (which they do in a process called photosynthesis ). Support their own weight (which animals usually do by means of a skeleton).
WebQuest Plant and Animal Cells Zunal.Com
4.5 Plant and Animal Cells WordPress.com
This is a basic illustration of a plant cell with major parts labeled. Labels include nucleus, chloroplast, cytoplasm, membrane, cell wall, and vacuole, and mitochondrion. Use it as a poster in your classroom or have students glue it into their science notebooks.
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Animal and Plant Cell Venn Diagram 6 Cell Organelles 7 The Animal Cell 8 If you think about it, your local community has many parts that allow it to function properly, just like an plant cell. Relate the functions of a plants cell’s organelles to parts of your community that have a similar function. Organelle Function of organelle in the cell Name a part of your school that has a similar
11/07/2012 · Plant cells have to perform two functions that are not required of animal cells: Produce their own food (which they do in a process called photosynthesis ). Support their own weight (which animals usually do by means of a skeleton).
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
WebQuest Plant and Animal Cells Zunal.Com
PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL PowerShow.com
This is a basic illustration of a plant cell with major parts labeled. Labels include nucleus, chloroplast, cytoplasm, membrane, cell wall, and vacuole, and mitochondrion. Use it as a poster in your classroom or have students glue it into their science notebooks.
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
I can label parts of animal and plant cells the tasks and functions of life. The Cell Theory All living organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The Cell Theory. ①Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus Examples: bacteria ②Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and
We will explore several interactive websites that will show us all the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. We will learn how to identify all the parts and differentiate between an animal cell and a plant cell. We will also learn the functions of all the parts of the cell. There are additional
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
4/09/2015 · the parts of the cell you learned about in this section. Use a check mark to indicate if the structure is found in animal cells, plant cells, or both. Provide a brief description of both the structure and function of the organelle. The nucleus is done as an example. Table 1 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Cell Movement Some cells need to move from place to place in their environment. …
Animal and Plant Cell Venn Diagram 6 Cell Organelles 7 The Animal Cell 8 If you think about it, your local community has many parts that allow it to function properly, just like an plant cell. Relate the functions of a plants cell’s organelles to parts of your community that have a similar function. Organelle Function of organelle in the cell Name a part of your school that has a similar
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
The student will distinguish between plant and animal cells. Day 1: Introduction to Plant Cells Objectives: Students will be able to correctly identify key parts on a cell. Students will be able to correctly identify plant cells. Students will be able to correctly identify animal cells. Materials: • Computer • Overhead • Plant cell pictures • Animal cell pictures • Diagram of cells
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells ThoughtCo
Grade 7 Science Unit 2 Plant and Animal Cells
Coloring the Animal Cell Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match.
and function of the organelles in plant and animal cells. Summary: This lesson is designed to teach the students about cell organelles and their functions within plant and animal cells.
the same function in both plant and animal cells. The cell membrane has transport proteins to assist the passage oflarger molecules or ionized molecUles. There are avariety ofother proteins embedded in the cell membrane. These are known as integralproteins. They help to maintain the structure ofthe cell membrane and other important functions. Sometimes the integral proteins have auxiliary
Title: PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL 1 PLANT CELL AND ANIMAL CELL. How do plant cells differ from animal cells? By Miss Caparos ; 2 Do Now. Identify the structures and state its function.
• Differentiate the characteristics of animal and plant cells • Identify and name at least six organelles in the cell • Match effectively the function to the organelle on a cell model • Build a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell . Introduction . Day One . Discuss Cell Theory . Formulation of the Cell Theory . In 1838, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden were enjoying
Depending upon the functions a plant cell contains certain special organelles which are absent in an animal cell like plastids and cell walls. Also, size and the number of organelles in a plant cell varies from an animal cell. For example, a plant cell contains large single vacuole but an animal cell contains small and very few vacuoles.
The plasmodesmata, pores in the cell wall that link adjacent cells and allow plant cells to communicate with adjacent cells. Animals have a different but functionally analogous system of gap junctions between adjacent cells.
The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). The nucleolus is found within the nucleus. Comparing Plant And Animal Cells VENN Diagram Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. Add descriptions to show the differences cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm shape nucleus
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells based on the organelles they share and that make them unique. Compare the organelles of a cell to parts of a city
Animal and Plant Cell Venn Diagram 6 Cell Organelles 7 The Animal Cell 8 If you think about it, your local community has many parts that allow it to function properly, just like an plant cell. Relate the functions of a plants cell’s organelles to parts of your community that have a similar function. Organelle Function of organelle in the cell Name a part of your school that has a similar
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and
CELL EXPLORATION ACTIVITIES nucleus, vacuoles, and even chloroplasts in the cells. Describe how you feel as you see parts of living things never before seengbyhanother human. Now, read “Seeing the First Cells” on page 9 of your tex bok and mi hpg rf R Hooke’s microscope and his drawing of cells! In t h es pacb l ow, y rfC T m g 10 u textbook. 1. _ 2. _ 3. _____!!!!! Cell Scientist
To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells ThoughtCo
CELLS kean.edu
Organelles found in both animal and plant cells: The cell membrane (or plasma membrane) is the ‘skin’ that surrounds the entire cell. This porous membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids (phospholipid bilayer). The membrane allows the passage of nonpolar and small uncharged polar molecules via diffusion, while other larger polar molecules and ions are able to enter the cell
We will explore several interactive websites that will show us all the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. We will learn how to identify all the parts and differentiate between an animal cell and a plant cell. We will also learn the functions of all the parts of the cell. There are additional
Animal and Plant Cell Venn Diagram 6 Cell Organelles 7 The Animal Cell 8 If you think about it, your local community has many parts that allow it to function properly, just like an plant cell. Relate the functions of a plants cell’s organelles to parts of your community that have a similar function. Organelle Function of organelle in the cell Name a part of your school that has a similar
The student will distinguish between plant and animal cells. Day 1: Introduction to Plant Cells Objectives: Students will be able to correctly identify key parts on a cell. Students will be able to correctly identify plant cells. Students will be able to correctly identify animal cells. Materials: • Computer • Overhead • Plant cell pictures • Animal cell pictures • Diagram of cells
Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students can match the correct picture to the control card and then find the label and description that matches the correct picture. *** Students can actually place the picture on top of the picture, description on top of the description
goes out, gives shape and support, plant cell, animal cell); understand and use the English expressions for describing the functions of the different parts of a cell, e.g., Different parts of a cell carry out different activities so that the cell can function normally. The nucleus is the place which controls the activities of a cell. It also contains DNA, which carries the information for
CELLS kean.edu
4.5 Plant and Animal Cells WordPress.com
This is a basic illustration of a plant cell with major parts labeled. Labels include nucleus, chloroplast, cytoplasm, membrane, cell wall, and vacuole, and mitochondrion. Use it as a poster in your classroom or have students glue it into their science notebooks.
Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial.
and function of the organelles in plant and animal cells. Summary: This lesson is designed to teach the students about cell organelles and their functions within plant and animal cells.
The cell of a human or plant is the smallest functional and structural unit. Everyone is taught about cells back in highschool. Now you are expected to be able …
Plant Cell and the other panel Animal Cell and draw a picture under each label representing the proper cell and its components. On the inside panel students should list the parts of each cell, and

To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles.
Biology Plant & Animal Cells III (Parts & Functions
CELLS kean.edu
Directions for Animal Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy