Cumulative probability distribution table pdf
The cumulative distribution function tables, for each value x = 1, 2, 3, 4, the probability of a result less than or equal to x.
Gauss) distribution. It finds widespread applications in almost every scientific It finds widespread applications in almost every scientific discipline, e.g., probability theory, the …
3 Table A1, continued. Binomial distribution p n x.05 .10 .15 .20 .25 .30 .35 .40 .45 .50 11 0 .5688 .3138 .1673 .0859 .0422 .0198 .0088 .0036 .0014 .0005
Variance, and Standard Deviation from a Probability Distribution Table Using Lists to Compute Expected Value, Variance, and Standard Deviation You can practice computing the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of a probability distribution table by using the spreadsheet capabilities of the List Editor. For example, consider the data in Display 6.11 and the calculations on …
Cumulative Probability distribution table for binomial distribution by rasel7azam
The inverse cumulative distribution function gives the value associated with a specific cumulative probability. Use the inverse CDF to determine the value of the variable associated with a specific probability.
Cumulative Binomial Probability Distribution This table computes the cumulative probability of obtaining x successes in n trials of a binomial experiment with probability of success p .
the easiest type because this is exactly what the binomial distribution table gives us! Find the probability of 6 successes: P(r = 6) = 0.032 (2) Find the probability of less than a …
Cumulative Binomial Probability Calculator. This calculator will compute cumulative probabilities for a binomial outcome, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring.
For each one you can calculate Probability Density Function (PDF) or Probability Mass Function (PMF), Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) and Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF), Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF-1) and Inverse Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF-1).
Standard Normal Cumulative Probability Table Cumulative probabilities for POSITIVE z-values are shown in the following table: Title: std normal table.xls Created Date: 4/23/2009 3:32:38 AM
Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table SESM

SIA2 Ch00-06 CN High School Math
Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table Table shows cumulative probability functions of Poisson Distribution with various α. Exam-ple: to find the probability P(X ≤ 3) where X has a Poisson Distribution with α = 2, look
Use the cumulative binomial probability table in the back of your book to find the probability that at most 1 of the 15 sampled has no health insurance. Solution. The probability that at most 1 has no health insurance can be written as P ( X ≤ 1).
Case 4: The normal distribution 8. Cumulative distributions and density functions 9. Sampling from distributions: population vs. sample Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 3. Random variables Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 4. Random Variables A random variable is what an outcome can be. It could also be a function of an outcome
𝑃 Tis a (discrete) probability distribution function (pdf or PDF) 𝑃 T=𝑃 = Texpresses the probability that = T A random variable that is distributed with pdf 𝑃is written as ~𝑃 Some properties of the pdf: 0 Q𝑃 T Q1 a probability is always between 0and 1 σ𝑥∈𝑆𝑃 T=1 the probabilities of all elementary outcomes add up to 1 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS (DISCRETE) A
Probability Density Function (PDF)¶ The PDF, or density of a continuous random variable, is a function that describes the relative likelihood for a random variable (X) to take on a given value (x).
Measuring Corporate Default Rates Summary Measurement of the probability of default for a corporate exposure over a given investment horizon is often the first step in credit risk modeling, management, and pricing. Many market practitioners base their parameter estimates on results reported in rating agency default studies. Although the comparability of default rates reported by the agencies

1 Table A1. Binomial distribution
Probability Distribution Table scribd.com
Binomial Distribution cumulative Pearson Education
Free Cumulative Binomial Probability Calculator Free
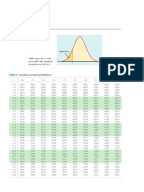
Standard Normal Distribution Table University of Florida

Statistical Tools Online Probability Distributions
Cumulative Probabilities Example SUNY Oswego

SIA2 Ch00-06 CN High School Math
Standard Normal Distribution Table University of Florida
Case 4: The normal distribution 8. Cumulative distributions and density functions 9. Sampling from distributions: population vs. sample Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 3. Random variables Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 4. Random Variables A random variable is what an outcome can be. It could also be a function of an outcome
Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table Table shows cumulative probability functions of Poisson Distribution with various α. Exam-ple: to find the probability P(X ≤ 3) where X has a Poisson Distribution with α = 2, look
Use the cumulative binomial probability table in the back of your book to find the probability that at most 1 of the 15 sampled has no health insurance. Solution. The probability that at most 1 has no health insurance can be written as P ( X ≤ 1).
the easiest type because this is exactly what the binomial distribution table gives us! Find the probability of 6 successes: P(r = 6) = 0.032 (2) Find the probability of less than a …
Measuring Corporate Default Rates Summary Measurement of the probability of default for a corporate exposure over a given investment horizon is often the first step in credit risk modeling, management, and pricing. Many market practitioners base their parameter estimates on results reported in rating agency default studies. Although the comparability of default rates reported by the agencies
Cumulative Binomial Probability Distribution This table computes the cumulative probability of obtaining x successes in n trials of a binomial experiment with probability of success p .
The inverse cumulative distribution function gives the value associated with a specific cumulative probability. Use the inverse CDF to determine the value of the variable associated with a specific probability.
For each one you can calculate Probability Density Function (PDF) or Probability Mass Function (PMF), Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) and Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF), Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF-1) and Inverse Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF-1).
The cumulative distribution function tables, for each value x = 1, 2, 3, 4, the probability of a result less than or equal to x.
Cumulative Probability distribution table for binomial distribution by rasel7azam
Probability Distribution Table scribd.com
SIA2 Ch00-06 CN High School Math
Case 4: The normal distribution 8. Cumulative distributions and density functions 9. Sampling from distributions: population vs. sample Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 3. Random variables Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 4. Random Variables A random variable is what an outcome can be. It could also be a function of an outcome
Cumulative Probability distribution table for binomial distribution by rasel7azam
The cumulative distribution function tables, for each value x = 1, 2, 3, 4, the probability of a result less than or equal to x.
Use the cumulative binomial probability table in the back of your book to find the probability that at most 1 of the 15 sampled has no health insurance. Solution. The probability that at most 1 has no health insurance can be written as P ( X ≤ 1).
𝑃 Tis a (discrete) probability distribution function (pdf or PDF) 𝑃 T=𝑃 = Texpresses the probability that = T A random variable that is distributed with pdf 𝑃is written as ~𝑃 Some properties of the pdf: 0 Q𝑃 T Q1 a probability is always between 0and 1 σ𝑥∈𝑆𝑃 T=1 the probabilities of all elementary outcomes add up to 1 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS (DISCRETE) A
Variance, and Standard Deviation from a Probability Distribution Table Using Lists to Compute Expected Value, Variance, and Standard Deviation You can practice computing the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of a probability distribution table by using the spreadsheet capabilities of the List Editor. For example, consider the data in Display 6.11 and the calculations on …
Free Cumulative Binomial Probability Calculator Free
Cumulative Probabilities Example SUNY Oswego
𝑃 Tis a (discrete) probability distribution function (pdf or PDF) 𝑃 T=𝑃 = Texpresses the probability that = T A random variable that is distributed with pdf 𝑃is written as ~𝑃 Some properties of the pdf: 0 Q𝑃 T Q1 a probability is always between 0and 1 σ𝑥∈𝑆𝑃 T=1 the probabilities of all elementary outcomes add up to 1 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS (DISCRETE) A
Measuring Corporate Default Rates Summary Measurement of the probability of default for a corporate exposure over a given investment horizon is often the first step in credit risk modeling, management, and pricing. Many market practitioners base their parameter estimates on results reported in rating agency default studies. Although the comparability of default rates reported by the agencies
Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table Table shows cumulative probability functions of Poisson Distribution with various α. Exam-ple: to find the probability P(X ≤ 3) where X has a Poisson Distribution with α = 2, look
Case 4: The normal distribution 8. Cumulative distributions and density functions 9. Sampling from distributions: population vs. sample Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 3. Random variables Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 4. Random Variables A random variable is what an outcome can be. It could also be a function of an outcome
Cumulative Binomial Probability Distribution This table computes the cumulative probability of obtaining x successes in n trials of a binomial experiment with probability of success p .
Variance, and Standard Deviation from a Probability Distribution Table Using Lists to Compute Expected Value, Variance, and Standard Deviation You can practice computing the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of a probability distribution table by using the spreadsheet capabilities of the List Editor. For example, consider the data in Display 6.11 and the calculations on …
Cumulative Probability distribution table for binomial distribution by rasel7azam
Standard Normal Cumulative Probability Table Cumulative probabilities for POSITIVE z-values are shown in the following table: Title: std normal table.xls Created Date: 4/23/2009 3:32:38 AM
Cumulative Probabilities Example SUNY Oswego
Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table SESM
Case 4: The normal distribution 8. Cumulative distributions and density functions 9. Sampling from distributions: population vs. sample Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 3. Random variables Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 4. Random Variables A random variable is what an outcome can be. It could also be a function of an outcome
Standard Normal Cumulative Probability Table Cumulative probabilities for POSITIVE z-values are shown in the following table: Title: std normal table.xls Created Date: 4/23/2009 3:32:38 AM
Cumulative Binomial Probability Calculator. This calculator will compute cumulative probabilities for a binomial outcome, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring.
the easiest type because this is exactly what the binomial distribution table gives us! Find the probability of 6 successes: P(r = 6) = 0.032 (2) Find the probability of less than a …
Variance, and Standard Deviation from a Probability Distribution Table Using Lists to Compute Expected Value, Variance, and Standard Deviation You can practice computing the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of a probability distribution table by using the spreadsheet capabilities of the List Editor. For example, consider the data in Display 6.11 and the calculations on …
Cumulative Binomial Probability Distribution This table computes the cumulative probability of obtaining x successes in n trials of a binomial experiment with probability of success p .
Cumulative Probability distribution table for binomial distribution by rasel7azam
The cumulative distribution function tables, for each value x = 1, 2, 3, 4, the probability of a result less than or equal to x.
Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table Table shows cumulative probability functions of Poisson Distribution with various α. Exam-ple: to find the probability P(X ≤ 3) where X has a Poisson Distribution with α = 2, look
𝑃 Tis a (discrete) probability distribution function (pdf or PDF) 𝑃 T=𝑃 = Texpresses the probability that = T A random variable that is distributed with pdf 𝑃is written as ~𝑃 Some properties of the pdf: 0 Q𝑃 T Q1 a probability is always between 0and 1 σ𝑥∈𝑆𝑃 T=1 the probabilities of all elementary outcomes add up to 1 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS (DISCRETE) A
For each one you can calculate Probability Density Function (PDF) or Probability Mass Function (PMF), Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) and Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF), Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF-1) and Inverse Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF-1).
The inverse cumulative distribution function gives the value associated with a specific cumulative probability. Use the inverse CDF to determine the value of the variable associated with a specific probability.
3 Table A1, continued. Binomial distribution p n x.05 .10 .15 .20 .25 .30 .35 .40 .45 .50 11 0 .5688 .3138 .1673 .0859 .0422 .0198 .0088 .0036 .0014 .0005
Gauss) distribution. It finds widespread applications in almost every scientific It finds widespread applications in almost every scientific discipline, e.g., probability theory, the …
Cumulative Probabilities Example SUNY Oswego
Probability Distribution Table scribd.com
Cumulative Binomial Probability Distribution This table computes the cumulative probability of obtaining x successes in n trials of a binomial experiment with probability of success p .
Measuring Corporate Default Rates Summary Measurement of the probability of default for a corporate exposure over a given investment horizon is often the first step in credit risk modeling, management, and pricing. Many market practitioners base their parameter estimates on results reported in rating agency default studies. Although the comparability of default rates reported by the agencies
𝑃 Tis a (discrete) probability distribution function (pdf or PDF) 𝑃 T=𝑃 = Texpresses the probability that = T A random variable that is distributed with pdf 𝑃is written as ~𝑃 Some properties of the pdf: 0 Q𝑃 T Q1 a probability is always between 0and 1 σ𝑥∈𝑆𝑃 T=1 the probabilities of all elementary outcomes add up to 1 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS (DISCRETE) A
The inverse cumulative distribution function gives the value associated with a specific cumulative probability. Use the inverse CDF to determine the value of the variable associated with a specific probability.
For each one you can calculate Probability Density Function (PDF) or Probability Mass Function (PMF), Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) and Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF), Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF-1) and Inverse Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF-1).
Gauss) distribution. It finds widespread applications in almost every scientific It finds widespread applications in almost every scientific discipline, e.g., probability theory, the …
the easiest type because this is exactly what the binomial distribution table gives us! Find the probability of 6 successes: P(r = 6) = 0.032 (2) Find the probability of less than a …
Cumulative Binomial Probability Calculator. This calculator will compute cumulative probabilities for a binomial outcome, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring.
3 Table A1, continued. Binomial distribution p n x.05 .10 .15 .20 .25 .30 .35 .40 .45 .50 11 0 .5688 .3138 .1673 .0859 .0422 .0198 .0088 .0036 .0014 .0005
Variance, and Standard Deviation from a Probability Distribution Table Using Lists to Compute Expected Value, Variance, and Standard Deviation You can practice computing the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of a probability distribution table by using the spreadsheet capabilities of the List Editor. For example, consider the data in Display 6.11 and the calculations on …
The cumulative distribution function tables, for each value x = 1, 2, 3, 4, the probability of a result less than or equal to x.
Use the cumulative binomial probability table in the back of your book to find the probability that at most 1 of the 15 sampled has no health insurance. Solution. The probability that at most 1 has no health insurance can be written as P ( X ≤ 1).
Standard Normal Cumulative Probability Table Cumulative probabilities for POSITIVE z-values are shown in the following table: Title: std normal table.xls Created Date: 4/23/2009 3:32:38 AM
Case 4: The normal distribution 8. Cumulative distributions and density functions 9. Sampling from distributions: population vs. sample Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 3. Random variables Session 2: Probability distributionsand density functions – p. 4. Random Variables A random variable is what an outcome can be. It could also be a function of an outcome


Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table Table shows cumulative probability functions of Poisson Distribution with various α. Exam-ple: to find the probability P(X ≤ 3) where X has a Poisson Distribution with α = 2, look
Cumulative Poisson Distribution Table SESM
1 Table A1. Binomial distribution