Drugs brains and behavior the science of addiction pdf
Aided by brain imaging advances, scientists are looking for evidence that compulsive nondrug behaviors lead to long-term changes in reward circuitry People toss around the term “addiction” to describe someone’s relationship to a job, a boyfriend, or a computer. But scientists have traditionally
Heads Up: Real News About Drugs and Your Body- Year 14-15 Compilation for Teachers Drogas: Derribemos los mitos ( Drugs: SHATTER THE MYTHS ) Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction
Addiction Is a Brain Disease, and It Matters Alan I. Leshner Scientific advances over the past 20 years have shown that drug addiction is a chronic, relapsing disease that results from the prolonged effects of drugs on the brain. As with many other brain diseases, addiction has embedded behavioral and social-context aspects that are important parts of the disorder itself. Therefore, the most
treating drug addiction. Behavioral treatments existed but were not yet in use. Today . Combined biological, epidemiological, and social science discoveries of the last 3 decades have given us a detailed understanding of the risks, mechanisms, and consequences of drug abuse and addiction. Because drug use typically begins in adolescence, we have targeted prevention and public outreach …
Provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that …
Some drugs can impair the brain’s ability to focus and think clearly. 5 Changes in behavior, such as the following, can indicate a problem with drug abuse: 4,6 Increased aggression or irritability.
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (National Institutes of Health, Aug. Hijacked Brains: The Experience and Science of Chronic Addiction Editorial Reviews. Review. “Barnes does a masterful job describing the science behind this complex chronic disease, as well as putting a human face on it [PDF]Hijacked Brains: The Experience And Science Of Chronic Addiction Download …
Drugs, Brains and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (NIDA) We have identified many of the biological and environmental factors and are beginning to search for the genetic variations that contribute to the development and progression of the disease.
addiction is a brain disease that develops over time as a result of the initially voluntary behavior of using drugs. The consequence is virtually uncontrollable compulsive drug craving, seeking,
The Brain—About NIH science.education.nih.gov
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ukFjH9odsXw

Hijacked Brains The Experience And Science Of Chronic
Drug addiction, also called substance use disorder, is a disease that affects a person’s brain and behavior and leads to an inability to control the use of a legal or illegal drug or medication. Substances such as alcohol, marijuana and nicotine also are considered drugs. When you’re addicted, you
Advances in brain imaging science make it possible to see inside the brain of an addicted person and pinpoint the parts of the brain affected by drugs of abuse — providing knowledge that will enable the development of new approaches to prevention and treatment.
Thomas J. Gould, Ph.D. The brain regions and neural processes that underlie addiction overlap extensively with those that support cognitive functions, including learning, memory, and reasoning. Drug activity in these regions and processes during early stages of abuse foster strong maladaptive
[NIDA] in its informative manual “ Drug, brain and behavior. The science of addiction” (NIDA, 2007). Many authors expanded and justifi ed it, especially Nora Volkow, Director of the NIDA since 2003, all of this coupled with generous funding of the studies in this vein. Also the American Psychiatric Association (2013) in the latest version of the DSM-5 consider substance consumption
Drug profiles in the margins provide a snapshot of the primary characteristics of a drug for quick and easy reference. Illustrations of common and novel research techniques in psychopharmacology, such as microdialysis, drug discrimination, and optogenetics, provide insights to important methods used in …
Drug-seeking refer to the craving aspect of addiction. Dopamine may be more involved in drug-seeking (craving) component of addiction. The opiate (endorphin), GABA, or glutamatergic systems may be more involved in pleasure-seeking aspect of addiction.
How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of Drug Addiction For much of the past century, scientists studying drugs and drug use labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions about the nature of addiction.
Check out our compiled list of resources from the CDC, White House, SAMHSA, and NIDA about drugs, substance abuse, addiction, and communities at risk.
These brain changes trigger the compulsive drug-seeking and drug-taking behaviors that are the hallmarks of drug addiction. NIDA’s scientists have clearly shown that drug abuse is a preventable behavior and drug addiction is a treatable brain disease. Among the many and diverse accomplishments over the past three decades, NIDA-supported research has
Drugs, brains, and behavior. The science of addiction. National Institutes of Health. NIH Pub No. 10‐5605. The science of addiction. National Institutes of Health.
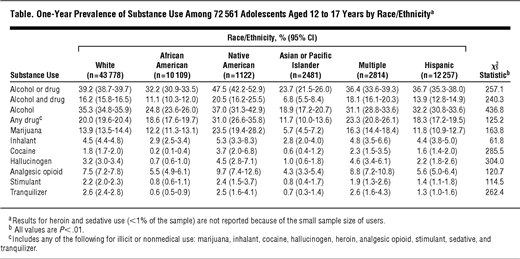
National Institute on Drug Abuse. Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction 2014 [cited 2016 December 29].
The way the brain responds to repeated substance abuse plays a big part in drug and alcohol addictions. The abuse of addictive substances activates the brain’s reward system. Frequently activating this system with drugs can lead to addiction. Learn how changes within the brain can affect your addiction.
Scientific advances over the past 20 years have shown that drug addiction is a chronic, relapsing disease that results from the prolonged effects of drugs on the brain. As with many other brain diseases, addiction has embedded behavioral and social-context aspects that are important parts of the disorder itself. Therefore, the most effective treatment approaches will include biological
Using drugs in your teen years can affect the way your brain develops. Using drugs can affect brain development and using them earlier in life can lead to a higher chance of developing a problem with drugs.
10/09/2014 · Addiction is a neurological disorder that affects the reward system in the brain. In a healthy person, the reward system reinforces important behaviors that are essential for …
Addiction is a chronic brain disorder and not simply a behavior problem involving alcohol, drugs, gambling or sex, experts contend in a new definition of addiction, one that is not solely related
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (National Institutes of Health, Aug. 2010). Polosa R, et al. “Treatment of Nicotine Addiction: Present Therapeutic Options and Pipeline Developments,” Trends in Pharmacological Sciences (Jan. 20, 2011): E-publication.
SHIFTING IDEOLOGIES Prescription Medications Legalization of Recreational Marijuana Impairment Free Workplace & Fit for Duty Policies Illicit Drugs
There’s a reason that teenagers act the way they do. Understanding the brain science behind teenage behavior can help parents better prepare their kids to avoid drugs and alcohol.
GMT drugs and behavior pdf – How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of Drug Addiction For much of the past century, scientists studying drugs and drug use labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions about the nature of addiction. When scientists began to study addictive behavior in the 1930s, people addicted to drugs were thought to be morally flawed and …

In the official publication “Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction,” NIDA director Nora Volkow writes, “Today, thanks to science, our views and our responses to drug abuse have changed dramatically.
Supported by a Science Education Drug Abuse Partnership Award (SEDAPA), from The National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health. Grant Number: R25DA15461 Grant Number: R25DA15461 The contents provided here are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NIH.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse has revised one of its foundational publications – Drugs, Brain and Behavior: The Science of Addiction. The online guidebook, also available as a pdf, provides a comprehensive guide to what NIDA does – improve the scientific understanding of addiction and
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction – Provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that have been developed to prevent and treat the
3/09/2016 · Drug addiction is a big problem in the U.S. But what exactly is going on in the brain when someone gets addicted? Subscribe for more videos: https://www.yout… But what exactly is …
New booklet explains addiction as a brain disease. Over the last decade, brain research has transformed our understanding of addiction. “Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction”–a 30-page, color booklet from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)–presents the latest findings on this topic.
addiction is considered a brain disease – one with imbedded behavioral and social context aspects. (” Science-Based Views of Drug Addiction and Its Treatment ,” can be found in The Journal of the American Medical
reventing and Treating Substance Use Disorders: A Comprehensive Approach First recognized as a disease in 1956 by the American Medical Association, until recently, little progress has been made in treating addiction as a chronic health condition. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), addiction is defined as a chronic, relapsing brain disease that is characterized by
Drugs, Brains, & Behavior — The Science of Addiction discusses the reasons people take drugs, why some people become addicted while others do not, how drugs work in the brain, and how addiction can be prevented and treated.
The Science of Addiction (Drugs and the Brain) (Hazelden, 1996), and Drugs, The Brain and Behavior (Haworth the presence of alcohol abuse and dependence, [PDF] The Tailed Head-hunters Of Nigeria;: An Account Of An Official’s Seven Years’ Experience In
https://youtube.com/watch?v=p0lL1MN2yCs
Drug Seeking and Cravings Addictions’ Effect on the Brain
Behavioral, which looks at the consequences of drug abuse on behavior and cognition, providing important information for the design of treatment and prevention interventions; and Neurobiological, which delves into the processes and mechanisms in the brain and nervous system underlying addiction.
Avoiding addiction-oriented behavior — whether you’re avoiding drugs or abstaining from gambling — is a key component of substance abuse recovery. There are several ways people in recovery can avoid relapse, but one of the most well-known is HALT. The acronym …
How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of DrTug Addiction hroughout much of the last century, scientists studying drug abuse labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions
SOURCES: National Institute on Drug Abuse: “The Science of Drug Abuse and Addiction: The Basics,” “Easy to Read Drug Facts,” “Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction
Drugs, Brains & Behavior – The Science of Addiction National Institute on Drug Abuse Updated July 2014. This booklet provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that have been developed to prevent and treat the disease.
This note explains the following topics related to addiction: risky use of addictive medicines, effective treatment, best treatment practices, treatment gap, addiction treatment workforce, addiction care, public attitudes about addiction and reform health care practices.
Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain Animation
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (National Institute on Drug Abuse) Also in Spanish FastStats: Illegal Drug Use (National Center for Health Statistics) Other Specific Populations (Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration)
Scientists are also examining the potential of vaccines against nicotine, cocaine, and other drugs, which might prevent the drug from entering the brain. “Addiction is a devastating disease, with a relatively high death rate and serious social consequences,” Volkow says.
* The science of drug addiction * How drugs change the way the teen brain works * How drugs change how the teen brain develops Coming Up in the Next Installment Teens, Drug Abuse, and AIDS: The Deadly Connection Assessment Quiz Use the Activity 1 Reproducible within as an Assessment Quiz to determine your students’ core base of knowledge and to test what they’ve learned about the …
Drug-infested high schools are also contributing to the problem. According to a survey by the National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse, nearly half of American high school students are aware of a student who sells drugs at their school.
Addiction and Cognition PubMed Central (PMC)

About Drugs and Addiction in Persons Who Inject Drugs CDC
https://youtube.com/watch?v=b4CBy0uVqRc
Addiction Disease Scholastic
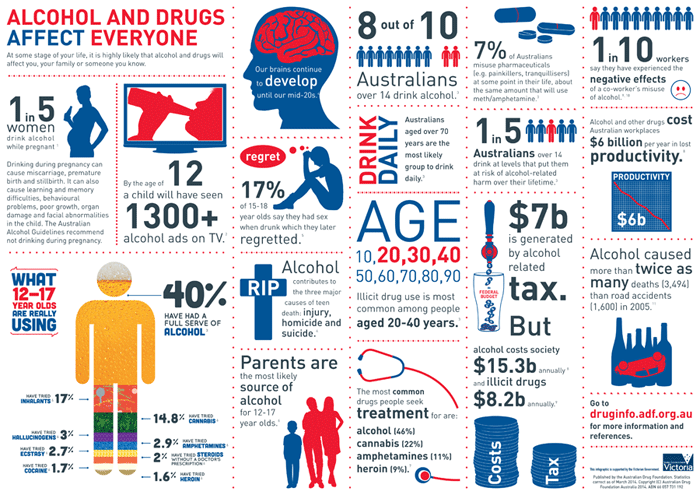
reventing and Treating Substance Use Disorders A
Drugs and the Future Brain Science Addiction and Society


https://youtube.com/watch?v=aOSD9rTVuWc
FRONTIERS IN NEUROSCIENCE THE SCIENCE OF SUBSTANCE
addiction is a disease of the brain Live Science
Addiction and Recovery – Addiction Treatment Forum

Addiction Community Resources Toolkit Chuck Fleischmann
https://youtube.com/watch?v=MBPBcJlZlsA
What Parents Need to Know About Marijuana Use and Teens
Addiction and Cognition PubMed Central (PMC)
addicton Books online free computer science ebooks
Drug-seeking refer to the craving aspect of addiction. Dopamine may be more involved in drug-seeking (craving) component of addiction. The opiate (endorphin), GABA, or glutamatergic systems may be more involved in pleasure-seeking aspect of addiction.
Supported by a Science Education Drug Abuse Partnership Award (SEDAPA), from The National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health. Grant Number: R25DA15461 Grant Number: R25DA15461 The contents provided here are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NIH.
Aided by brain imaging advances, scientists are looking for evidence that compulsive nondrug behaviors lead to long-term changes in reward circuitry People toss around the term “addiction” to describe someone’s relationship to a job, a boyfriend, or a computer. But scientists have traditionally
These brain changes trigger the compulsive drug-seeking and drug-taking behaviors that are the hallmarks of drug addiction. NIDA’s scientists have clearly shown that drug abuse is a preventable behavior and drug addiction is a treatable brain disease. Among the many and diverse accomplishments over the past three decades, NIDA-supported research has
Provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that …
National Institute on Drug Abuse. Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction 2014 [cited 2016 December 29].
Heads Up: Real News About Drugs and Your Body- Year 14-15 Compilation for Teachers Drogas: Derribemos los mitos ( Drugs: SHATTER THE MYTHS ) Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction
Recovery from Addiction Living Sober After Treatment
Drugs and the Future Brain Science Addiction and Society
Avoiding addiction-oriented behavior — whether you’re avoiding drugs or abstaining from gambling — is a key component of substance abuse recovery. There are several ways people in recovery can avoid relapse, but one of the most well-known is HALT. The acronym …
Thomas J. Gould, Ph.D. The brain regions and neural processes that underlie addiction overlap extensively with those that support cognitive functions, including learning, memory, and reasoning. Drug activity in these regions and processes during early stages of abuse foster strong maladaptive
Drug-seeking refer to the craving aspect of addiction. Dopamine may be more involved in drug-seeking (craving) component of addiction. The opiate (endorphin), GABA, or glutamatergic systems may be more involved in pleasure-seeking aspect of addiction.
Drugs, Brains & Behavior – The Science of Addiction National Institute on Drug Abuse Updated July 2014. This booklet provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that have been developed to prevent and treat the disease.
The way the brain responds to repeated substance abuse plays a big part in drug and alcohol addictions. The abuse of addictive substances activates the brain’s reward system. Frequently activating this system with drugs can lead to addiction. Learn how changes within the brain can affect your addiction.
Aided by brain imaging advances, scientists are looking for evidence that compulsive nondrug behaviors lead to long-term changes in reward circuitry People toss around the term “addiction” to describe someone’s relationship to a job, a boyfriend, or a computer. But scientists have traditionally
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction – Provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that have been developed to prevent and treat the
Drug addiction, also called substance use disorder, is a disease that affects a person’s brain and behavior and leads to an inability to control the use of a legal or illegal drug or medication. Substances such as alcohol, marijuana and nicotine also are considered drugs. When you’re addicted, you
Drugs, Brains and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (NIDA) We have identified many of the biological and environmental factors and are beginning to search for the genetic variations that contribute to the development and progression of the disease.
Behavioral, which looks at the consequences of drug abuse on behavior and cognition, providing important information for the design of treatment and prevention interventions; and Neurobiological, which delves into the processes and mechanisms in the brain and nervous system underlying addiction.
How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of Drug Addiction For much of the past century, scientists studying drugs and drug use labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions about the nature of addiction.
addicton Books online free computer science ebooks
Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain Animation
Advances in brain imaging science make it possible to see inside the brain of an addicted person and pinpoint the parts of the brain affected by drugs of abuse — providing knowledge that will enable the development of new approaches to prevention and treatment.
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (National Institute on Drug Abuse) Also in Spanish FastStats: Illegal Drug Use (National Center for Health Statistics) Other Specific Populations (Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration)
The Science of Addiction (Drugs and the Brain) (Hazelden, 1996), and Drugs, The Brain and Behavior (Haworth the presence of alcohol abuse and dependence, [PDF] The Tailed Head-hunters Of Nigeria;: An Account Of An Official’s Seven Years’ Experience In
Drug-infested high schools are also contributing to the problem. According to a survey by the National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse, nearly half of American high school students are aware of a student who sells drugs at their school.
This note explains the following topics related to addiction: risky use of addictive medicines, effective treatment, best treatment practices, treatment gap, addiction treatment workforce, addiction care, public attitudes about addiction and reform health care practices.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse has revised one of its foundational publications – Drugs, Brain and Behavior: The Science of Addiction. The online guidebook, also available as a pdf, provides a comprehensive guide to what NIDA does – improve the scientific understanding of addiction and
Addiction Is a Brain Disease, and It Matters Alan I. Leshner Scientific advances over the past 20 years have shown that drug addiction is a chronic, relapsing disease that results from the prolonged effects of drugs on the brain. As with many other brain diseases, addiction has embedded behavioral and social-context aspects that are important parts of the disorder itself. Therefore, the most
Avoiding addiction-oriented behavior — whether you’re avoiding drugs or abstaining from gambling — is a key component of substance abuse recovery. There are several ways people in recovery can avoid relapse, but one of the most well-known is HALT. The acronym …
GMT drugs and behavior pdf – How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of Drug Addiction For much of the past century, scientists studying drugs and drug use labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions about the nature of addiction. When scientists began to study addictive behavior in the 1930s, people addicted to drugs were thought to be morally flawed and …
Drugs, Brains & Behavior – The Science of Addiction National Institute on Drug Abuse Updated July 2014. This booklet provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that have been developed to prevent and treat the disease.
SOURCES: National Institute on Drug Abuse: “The Science of Drug Abuse and Addiction: The Basics,” “Easy to Read Drug Facts,” “Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction
Hijacked Brains The Experience And Science Of Chronic
Drugs and the Future Brain Science Addiction and Society
The National Institute on Drug Abuse has revised one of its foundational publications – Drugs, Brain and Behavior: The Science of Addiction. The online guidebook, also available as a pdf, provides a comprehensive guide to what NIDA does – improve the scientific understanding of addiction and
Drugs, Brains, & Behavior — The Science of Addiction discusses the reasons people take drugs, why some people become addicted while others do not, how drugs work in the brain, and how addiction can be prevented and treated.
Scientists are also examining the potential of vaccines against nicotine, cocaine, and other drugs, which might prevent the drug from entering the brain. “Addiction is a devastating disease, with a relatively high death rate and serious social consequences,” Volkow says.
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (National Institutes of Health, Aug. Hijacked Brains: The Experience and Science of Chronic Addiction Editorial Reviews. Review. “Barnes does a masterful job describing the science behind this complex chronic disease, as well as putting a human face on it [PDF]Hijacked Brains: The Experience And Science Of Chronic Addiction Download …
10/09/2014 · Addiction is a neurological disorder that affects the reward system in the brain. In a healthy person, the reward system reinforces important behaviors that are essential for …
Drugs, brains, and behavior. The science of addiction. National Institutes of Health. NIH Pub No. 10‐5605. The science of addiction. National Institutes of Health.
treating drug addiction. Behavioral treatments existed but were not yet in use. Today . Combined biological, epidemiological, and social science discoveries of the last 3 decades have given us a detailed understanding of the risks, mechanisms, and consequences of drug abuse and addiction. Because drug use typically begins in adolescence, we have targeted prevention and public outreach …
Provides scientific information about the disease of drug addiction, including the many harmful consequences of drug abuse and the basic approaches that …
Drug addiction, also called substance use disorder, is a disease that affects a person’s brain and behavior and leads to an inability to control the use of a legal or illegal drug or medication. Substances such as alcohol, marijuana and nicotine also are considered drugs. When you’re addicted, you
Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain Animation
Addiction and Recovery – Addiction Treatment Forum
Scientific advances over the past 20 years have shown that drug addiction is a chronic, relapsing disease that results from the prolonged effects of drugs on the brain. As with many other brain diseases, addiction has embedded behavioral and social-context aspects that are important parts of the disorder itself. Therefore, the most effective treatment approaches will include biological
The way the brain responds to repeated substance abuse plays a big part in drug and alcohol addictions. The abuse of addictive substances activates the brain’s reward system. Frequently activating this system with drugs can lead to addiction. Learn how changes within the brain can affect your addiction.
How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of DrTug Addiction hroughout much of the last century, scientists studying drug abuse labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions
Advances in brain imaging science make it possible to see inside the brain of an addicted person and pinpoint the parts of the brain affected by drugs of abuse — providing knowledge that will enable the development of new approaches to prevention and treatment.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse has revised one of its foundational publications – Drugs, Brain and Behavior: The Science of Addiction. The online guidebook, also available as a pdf, provides a comprehensive guide to what NIDA does – improve the scientific understanding of addiction and
New booklet explains addiction as a brain disease. Over the last decade, brain research has transformed our understanding of addiction. “Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction”–a 30-page, color booklet from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)–presents the latest findings on this topic.
Drugs, Brains, & Behavior — The Science of Addiction discusses the reasons people take drugs, why some people become addicted while others do not, how drugs work in the brain, and how addiction can be prevented and treated.
In the official publication “Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction,” NIDA director Nora Volkow writes, “Today, thanks to science, our views and our responses to drug abuse have changed dramatically.
How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of Drug Addiction For much of the past century, scientists studying drugs and drug use labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions about the nature of addiction.
Aided by brain imaging advances, scientists are looking for evidence that compulsive nondrug behaviors lead to long-term changes in reward circuitry People toss around the term “addiction” to describe someone’s relationship to a job, a boyfriend, or a computer. But scientists have traditionally
Avoiding addiction-oriented behavior — whether you’re avoiding drugs or abstaining from gambling — is a key component of substance abuse recovery. There are several ways people in recovery can avoid relapse, but one of the most well-known is HALT. The acronym …
Supported by a Science Education Drug Abuse Partnership Award (SEDAPA), from The National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health. Grant Number: R25DA15461 Grant Number: R25DA15461 The contents provided here are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NIH.
